ভূমিকা
In today’s hyper-connected world, ইন্টারনেট বেতার অনুভব করে, তাত্ক্ষণিক, এবং সর্বব্যাপী. তবে, প্রতিটি আন্তর্জাতিক ভিডিও কলের পিছনে, মেঘ লেনদেন, আর্থিক বাণিজ্য, and streaming service lies a critical yet often invisible infrastructure: দ submarine fiber optic cable.
ক submarine fiber optic cable is the backbone of global communications, carrying over 99% of international data traffic across oceans and seas. Without these undersea cable systems, global internet connectivity, international telecommunications, and cross-border data exchange would be nearly impossible.
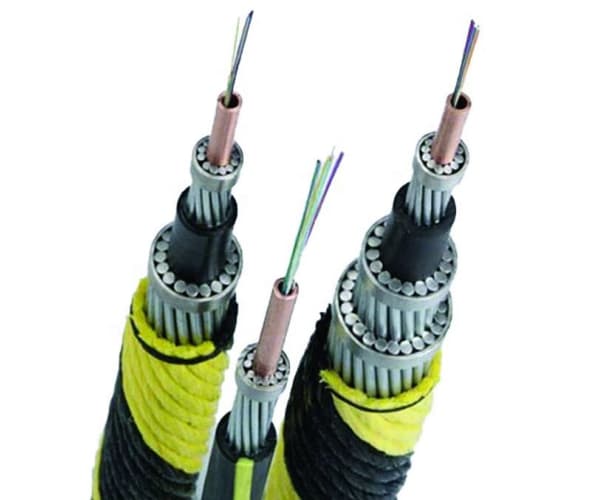

What Is a Submarine Fiber Optic Cable?
ক submarine fiber optic cable is a specially engineered cable laid on the seabed or buried beneath it to transmit data between countries and continents using optical fiber technology.
Also known as:
- সমুদ্রের নিচের ফাইবার অপটিক তার
- Subsea fiber optic cable
- সাবমেরিন যোগাযোগ তার
- Underwater fiber optic cable
- International fiber optic cable system
These cables use pulses of light transmitted through optical fibers to carry enormous volumes of data at extremely high speeds over thousands of kilometers.
How Submarine Fiber Optic Cables Work
At their core, submarine fiber optic cables operate on the same principles as terrestrial fiber optic cables, but with enhanced protection and durability to survive harsh ocean environments.
Optical Signal Transmission
Data is converted into light signals and transmitted through single-mode optical fibers. These signals travel at near the speed of light and experience minimal signal loss.
Optical Repeaters
Because light signals weaken over long distances, optical repeaters (also called undersea amplifiers) are installed every 50–100 km along the cable route. These repeaters boost the signal without converting it back to electrical form.
Cable Landing Stations
Each submarine cable connects to cable landing stations, where undersea networks interface with terrestrial fiber optic infrastructure. These stations are critical hubs in the global internet ecosystem.
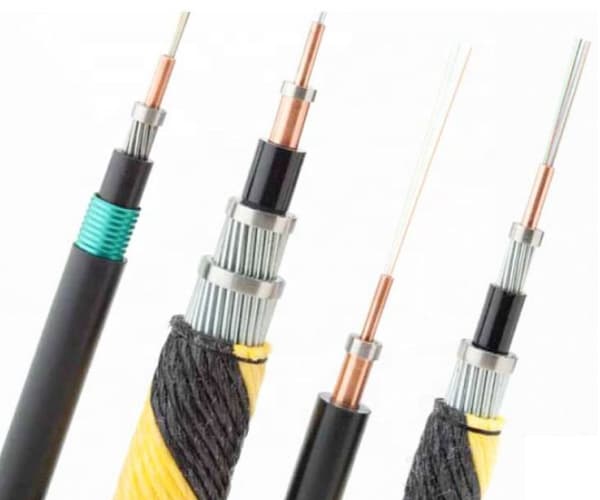

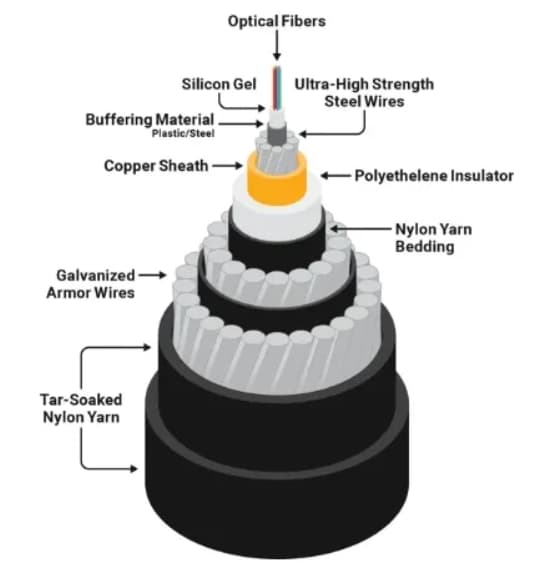
একটি সাবমেরিন ফাইবার অপটিক তারের গঠন
A modern submarine fiber optic cable system consists of multiple protective layers designed to withstand pressure, ক্ষয়, fishing activity, and geological hazards.
Typical Cable Layers
- Optical fibers – Carry the data signals
- Gel or water-blocking compound – Prevents water ingress
- Steel strength members – Provide tensile strength
- Copper or aluminum conductor – Supplies power to repeaters
- Polycarbonate insulation – Electrical protection
- Steel wire armoring – Protection against external damage
- Polyethylene outer sheath – Corrosion resistance
Near shore, armored submarine cables are used, while deep-sea sections typically use lighter, unarmored cables.
Types of Submarine Fiber Optic Cables
1. Shallow Water Submarine Cables
These cables operate near coastlines and are exposed to higher risks such as ship anchors and fishing trawlers. They are heavily armored and often buried beneath the seabed.
2. Deep-Sea Submarine Cables
Deep-sea cables lie thousands of meters below the surface, where human activity is minimal. These cables are lighter and designed for long-distance transmission.
3. Branching Unit Cable Systems
Modern submarine networks often include branching units that allow a single main cable to serve multiple destinations, improving flexibility and cost efficiency.
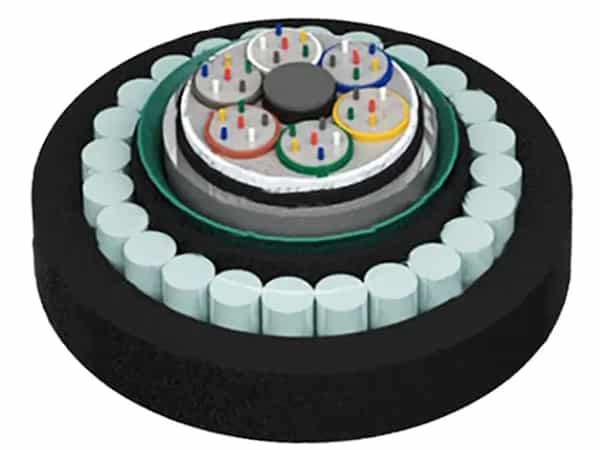

Why Submarine Fiber Optic Cables Are Important
গ্লোবাল ইন্টারনেটের মেরুদণ্ড
ওভার 1.4 million kilometers of submarine fiber optic cables span the oceans, connecting continents and enabling:
- International internet traffic
- Global cloud computing
- Financial market transactions
- Video streaming and content delivery
Low Latency and High Capacity
Compared to satellite communications, undersea fiber optic cables offer:
- Much lower latency
- Far higher bandwidth
- Greater reliability
This makes them essential for data-intensive applications such as AI, fintech, and real-time communications.
Submarine Fiber Optic Cable vs Satellite Communication
| বৈশিষ্ট্য | সাবমেরিন ফাইবার অপটিক কেবল | Satellite |
|---|---|---|
| Latency | Very low | উচ্চ |
| Bandwidth | Extremely high | Limited |
| নির্ভরযোগ্যতা | Stable | Weather-dependent |
| Cost per bit | কম | উচ্চ |
এই কারণে, submarine cable systems carry the vast majority of global data traffic.
Submarine Fiber Optic Cable Installation Process
রুট সার্ভে এবং পরিকল্পনা
ইনস্টলেশনের আগে, marine surveys analyze:
- Seabed topography
- Geological risks
- পরিবেশগত প্রভাব
Cable Laying
Specialized cable-laying ships deploy the submarine cable across the ocean floor with precision GPS navigation.
Burial and Protection
In shallow waters, plowing or jetting machines bury cables to protect them from external damage.
Testing and Commissioning
Once installed, the cable undergoes extensive testing to ensure signal integrity and performance.
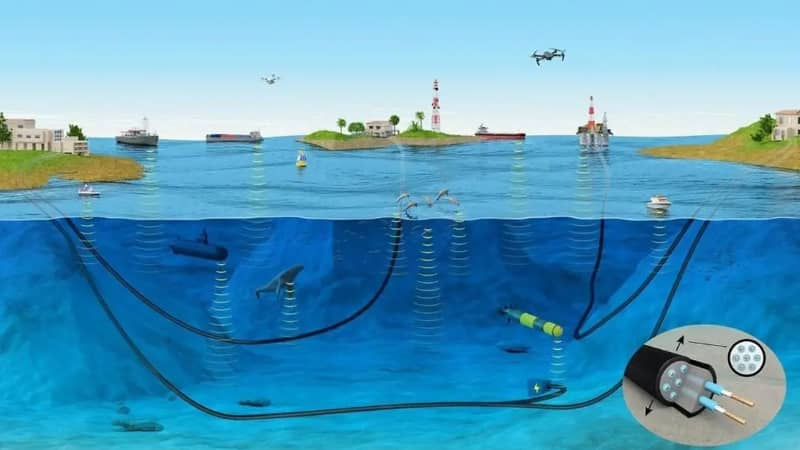

Maintenance and Repair of Submarine Cables
Despite their durability, submarine fiber optic cables can be damaged by earthquakes, fishing gear, or anchors.
Repair Process
- Fault detection using optical testing
- Dispatch of repair vessels
- Cable recovery and splicing
- Re-deployment and testing
Efficient maintenance is essential to minimize downtime in global communication networks.
Major Applications of Submarine Fiber Optic Cables
- International telecommunications
- Internet backbone infrastructure
- Cloud data center interconnection
- Offshore energy platforms
- Scientific ocean research
These applications highlight the strategic importance of submarine fiber optic cable networks.
Who Owns and Operates Submarine Fiber Optic Cables?
Submarine cables are typically owned by:
- Telecommunications companies
- Internet content providers
- Consortiums of multiple operators
In recent years, major cloud companies have invested heavily in private submarine cable systems to secure bandwidth and reduce latency.
Future Trends in Submarine Fiber Optic Cable Technology
Higher Fiber Counts
New cables support hundreds of fiber pairs, dramatically increasing capacity.
Space Division Multiplexing (SDM)
SDM technology allows more parallel data paths, improving efficiency and scalability.
Green and Energy-Efficient Systems
Modern undersea cables are designed to reduce power consumption and environmental impact.
Challenges Facing Submarine Fiber Optic Cables
- Geopolitical risks
- Natural disasters
- High installation costs
- Environmental regulations
এসব চ্যালেঞ্জ সত্ত্বেও, submarine cable systems remain indispensable.
Submarine Fiber Optic Cables and Global Digital Economy
From international banking to social media and e-commerce, submarine fiber optic cables enable:
- Cross-border trade
- Digital globalization
- Real-time global collaboration
They are a foundational element of the modern digital economy.
Submarine fiber optic cable
তাই, what is submarine fiber optic cable? It is the unseen yet indispensable infrastructure that powers global communication. These undersea fiber optic cable systems connect continents, support the internet, and enable the modern digital economy to function seamlessly.
As data demand continues to grow, submarine fiber optic cables will remain the most reliable, দক্ষ, and scalable solution for international connectivity. Understanding their structure, operation, and importance is essential for anyone involved in telecommunications, networking, or digital infrastructure.
By investing in knowledge and innovation around submarine fiber optic cable technology, the world continues to stay connected—across oceans, borders, and generations.
