Introdução
In today’s digital world, people send data across the globe in seconds. Emails, video calls, online payments, and cloud services all depend on one key technology: o submarine cable. A submarine cable is a physical cable that runs along the ocean floor and connects countries and continents.
Although many people believe satellites power the internet, this is not true. In fact, more than 95% of international data traffic travels through submarine communication cables. Como resultado, submarine cables form the true backbone of global communication.
You will learn what a submarine cable is, how it works, and why it matters. Além disso, the article explains submarine cable types, estrutura, instalação, risks, formulários, and future trends in simple and clear language.
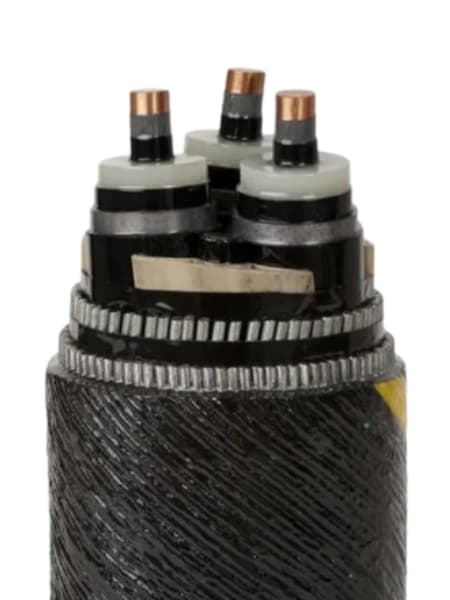

O que é um cabo submarino?
UM submarine cable, also called an undersea cable ou subsea cable, is a cable placed on the seabed to transmit data or electricity between land locations. Most modern submarine cables carry internet and communication signals using fiber optic technology.
People also use the following terms for submarine cables:
- Cabo de comunicação submarino
- Cabo de fibra óptica submarino
- Subsea telecom cable
- Fiber optic submarine cable
- International submarine cable system
Although the names differ, they usually describe the same system. These cables connect landing stations on land and allow data to move quickly across oceans.
A Short History of Submarine Cables
To understand submarine cables today, it helps to look at their history.
Em 1851, engineers laid the first successful submarine telegraph cable across the English Channel. Soon after, countries attempted longer connections. Em 1858, the first transatlantic cable connected Europe and North America. No entanto, early cables often failed because of poor insulation and weak signal strength.
Later, engineers improved materials and added repeaters to boost signals. Como resultado, submarine cables became more reliable.
In the late 20th century, fiber optic technology changed everything. Fiber optic submarine cables replaced copper cables and increased capacity by thousands of times. Today, a single submarine cable can transmit terabits of data per second.

Why Submarine Cables Matter
Submarine cables play a critical role in modern life. Without them, global communication would slow down or stop.
Espinha dorsal da Internet Global
First of all, submarine cables carry most international internet traffic. While satellites help in remote areas, they cannot match the speed or capacity of fiber optic submarine cables.
Because submarine cables use light signals, they offer fast and stable connections. Portanto, internet users experience low latency and high reliability.
Support for the Global Economy
Além disso, submarine cables support international trade and finance. Banks, stock markets, and payment systems rely on fast data connections. Even small delays can cause financial losses. Como resultado, financial institutions depend heavily on undersea cable networks.
Cloud Computing and Data Centers
Além disso, cloud services rely on submarine cables to link data centers in different countries. Without these cables, global cloud platforms would not function properly.
National and Strategic Importance
Finalmente, governments consider submarine cable systems as critical infrastructure. They protect and regulate them because national security and economic stability depend on reliable connectivity.

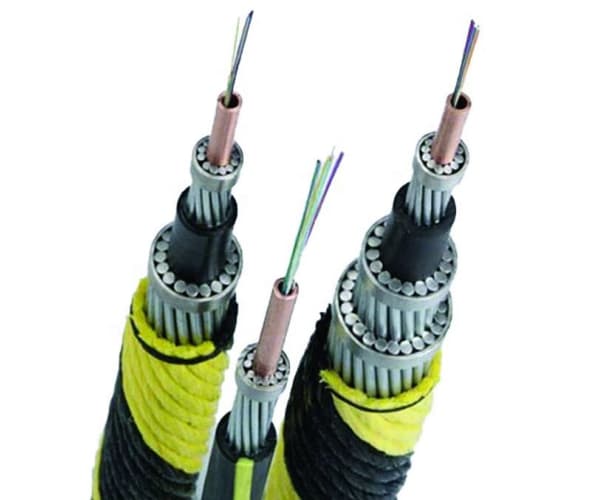
Types of Submarine Cables
Submarine cables serve different purposes. Portanto, engineers classify them into several types.
Submarine Communication Cables
Submarine communication cables transmit data such as internet traffic, voice calls, and video signals. Today, almost all new systems use fiber optic technology.
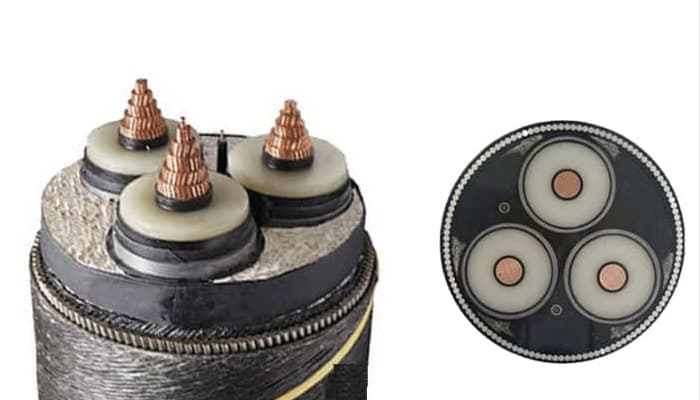
Cabos de alimentação submarinos
Submarine power cables carry electricity across water. Por exemplo, they connect islands to mainland power grids or link offshore wind farms to land-based substations.
Copper vs Fiber Optic Submarine Cables
In the past, copper submarine cables carried electrical signals. No entanto, they had low capacity and high signal loss.
In contrast, fiber optic submarine cables transmit data as light. Portanto, they offer much higher bandwidth, longer distance, and better performance. Como resultado, fiber optic systems dominate modern submarine cable networks.
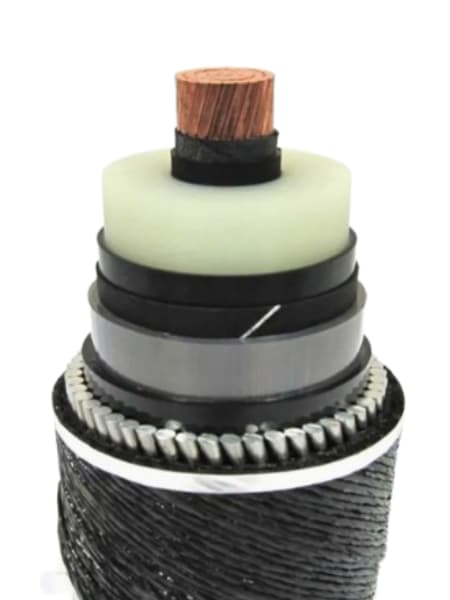
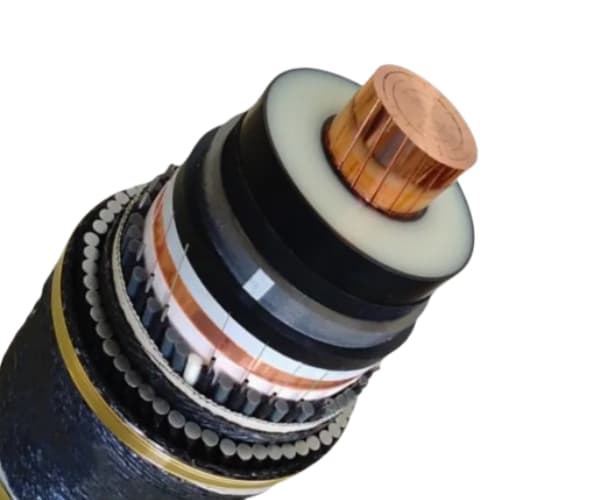
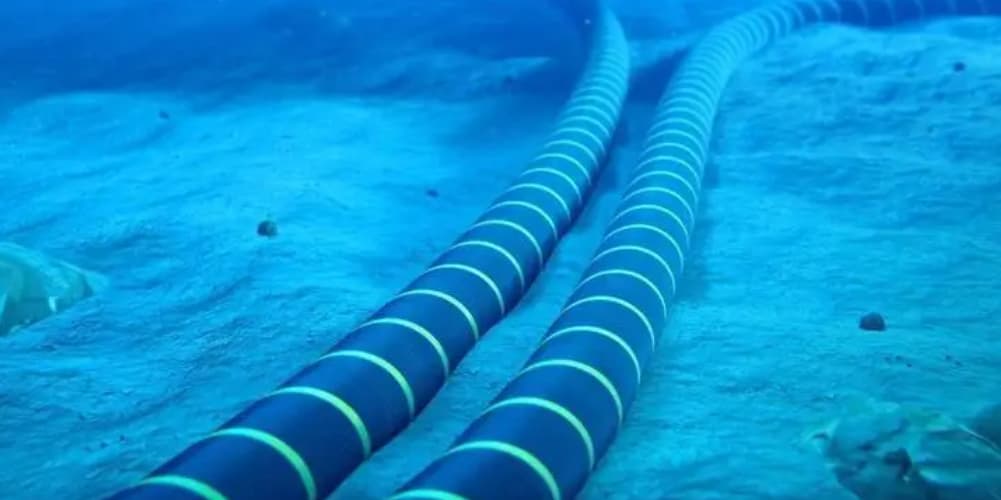
Estrutura de um cabo de fibra óptica submarino
A submarine fiber optic cable contains multiple layers. Each layer serves a specific purpose and protects the cable in harsh ocean conditions.
Optical Fiber Core
At the center of the cable, optical fibers carry data as light pulses. These fibers use ultra-pure glass to minimize signal loss.
Strength Members
Próximo, steel wires surround the fiber core. These wires provide strength and allow the cable to withstand tension during installation and operation.
Power Conductor
Além disso, a copper or aluminum conductor supplies power to repeaters along the cable route.
Insulation Layers
Plastic insulation layers protect the cable from seawater and electrical damage. They also improve durability.
Outer Armor
Finalmente, cables in shallow water include steel armor. This armor protects the cable from anchors, fishing nets, and seabed movement.

How Submarine Cables Work
Submarine fiber optic cables use light to transmit data. This process remains simple but highly efficient.
Data Transmission
Primeiro, transmitters convert data into light signals. These signals travel through the optical fibers using reflection inside the glass.
Signal Amplification
Over long distances, light signals weaken. Portanto, engineers install optical repeaters along the cable. These repeaters amplify the signal without converting it back to electricity.
Landing Stations
At both ends of the cable, landing stations connect the submarine cable to land-based networks. From there, data moves through terrestrial fiber networks to cities and data centers.
Submarine Cable Installation Process
Installing a submarine cable requires careful planning and specialized equipment.
Route Planning and Survey
Antes da instalação, survey teams map the seabed. They identify risks such as underwater mountains, fault lines, and human activities. Como resultado, engineers choose the safest and most efficient route.
Cable Manufacturing
Factories manufacture submarine cables in long sections. Then, crews coil the cable inside large tanks on cable-laying ships.
Cable Laying at Sea
During installation, the ship slowly releases the cable along the planned route. In deep water, the cable rests on the seabed. No entanto, in shallow areas, machines bury the cable for protection.
Shore-End Landing
Landing the cable near the coast is the most complex step. Crews work with local authorities and environmental agencies to complete this process safely.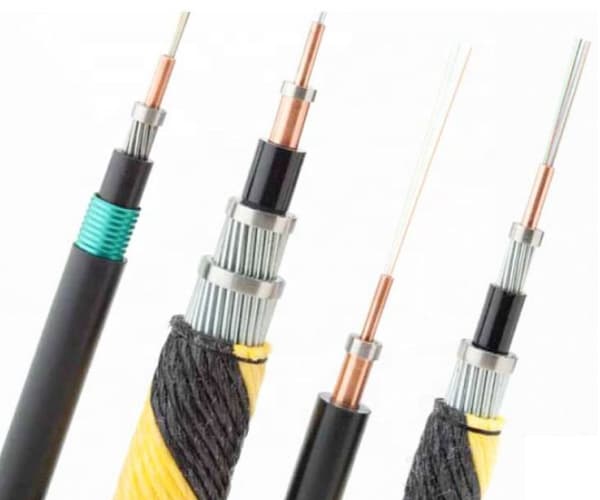
Risks and Challenges of Submarine Cables
Although submarine cables are reliable, they face several risks.
Human Activities
Fishing equipment and ship anchors cause most cable damage. Portanto, operators protect shallow-water cables with burial and armor.
Natural Disasters
Earthquakes and underwater landslides can damage submarine cable routes. This risk increases in tectonic regions.
Repair Complexity
When a cable breaks, repair ships must locate and lift the damaged section. This process takes time and costs money. Consequentemente, outages can last weeks.
Geopolitical Issues
Submarine cables cross international waters. Como resultado, security and political concerns sometimes affect cable routes and ownership.
Advantages of Submarine Fiber Optic Cables
Apesar desses desafios, submarine cables offer major advantages.
High Capacity
Modern systems carry massive data volumes. Portanto, they meet growing global demand.
Low Latency
Direct fiber routes reduce delay. Como resultado, applications like video calls and online trading work smoothly.
Longa vida útil
Most submarine cables operate for 25 years or more. Proper design ensures long-term reliability.
Eficiência de custos
Although installation costs are high, submarine cables offer low cost per data unit over time.

Submarine Cable vs Satellite Communication
Submarine cables and satellites serve different needs.
- Submarine cables provide high speed and low latency.
- Satellites offer wide coverage but higher delay.
Portanto, submarine communication cables handle most international traffic, while satellites support remote and backup services.
Applications of Submarine Cables
Submarine cables support many industries.
Internet and Telecom
They enable international internet access, voice calls, and streaming services.
Finance
Banks and stock markets rely on fast undersea connections.
Energy Sector
Submarine power cables connect offshore energy projects to land.
Government and Defense
Secure communication systems often use dedicated submarine cable networks.
Impacto ambiental
Modern submarine cable projects follow strict environmental rules.
- Engineers avoid sensitive habitats.
- Installation causes limited disturbance.
- Long-term impact remains minimal.
Como resultado, submarine cables coexist well with marine ecosystems.
Future Trends in Submarine Cable Systems
Global data demand continues to rise. Portanto, submarine cable technology keeps evolving.
Higher Capacity Cables
New designs include more fiber pairs and advanced transmission methods.
Private Cable Networks
Large technology companies now build private submarine cables to support cloud services.
Improved Monitoring
Real-time monitoring systems help detect faults faster and improve security.
Cabo Submarino
UM submarine cable is one of the most important technologies in the modern world. It connects continents, supports the global internet, and powers international communication. Although people rarely see these cables, daily life depends on them.
As data demand grows, submarine communication cables will remain essential. Through innovation and careful planning, these undersea networks will continue to connect the world for decades to come.
Please contact us for Fabricante de cabos submarinos!
